For Steam System : Kinds of Steam Trap
1. Classification by Model
| Major classification | Operation principle | Inside classification | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical steam trap |
Specific gravity difference of steam and condensate | Bucket type - Internal bucket type - Bucket type |
- Exhaust performance is good.
- Structure is easy. Service life is long. - Enduring a water hammer. - Small steam leakage. - Intermittent discharge which is excellent in durability. |
| Float type - Float type with lever |
- Quiet operation.
- Continuous discharge. - Small steam leakage. - Low tolerance for water hammer. |
||
| Thermostatic steam trap |
Difference in temperature of steam and condensate | Bellows type Bimetal type |
- Discharge condensate temperature is controllable.
- Exhaust performance is good. - No failure of valve closure. - Quiet operation. - Enduring water hammer. |
| Thermodynamic steam trap |
Thermodynamic characteristic difference of steam and condensate |
Disc type - Open air cooling type. - Air insulation type. |
- Simple structure. - Small and lightweight. - Usable for overheated steam. - Enduring water hammer. |
Mechanical steam trap

Inverted bucket type

Float type with lever
Thermostatic steam trap

Bimetal type

Bellows type
Thermodynamic steam trap
Disc type

Air insulation type
2. Operation Principle, Merit and Demerit
(1) Inverted bucket type steam trap
Operation principle

Bucket descends by its own weight and located in the bottom of a trap, and the valve opens fully. Condensate which flows into a main body fills a bucket and a main body, and excessive condensate is discharged through the valve of full open.
[Caution]
At the time of initial attachment, shut the stop valve on piping, accumulate condensate, and start the trap after making this condensate full in a trap and performing water seal.

Mixture of steam, air and gas flows into the trap and accumulates on upper portion of the bucket.
When this mixture reaches at a certain amount (about 2 / 3 of the bucket), the bucket is lifted with buoyancy, then closing the valve. Without influx of condensate the trap keeps closing.

When condensate flows into the trap again, the steam condenses inside the bucket, increasing the level of liquid in the bucket. This velocity is moderated by inflow of condensate. In addition, air and other gases in the bucket is discharged through an air vent at the upper part of the bucket, and accumulates at the upper part of the trap. While steam is discharged from the air vent, air rises in the condensate as very fine bubbles by difference in specific gravity due to no pressure difference in the body. Since it condenses before reaching the top of the trap, no steam loss is caused.

The influx of condensate keeps rising of liquid level by condense of steam in the bucket. When the liquid level exceeds a certain level (about 1 / 3 of the bucket) the bucket loses buoyancy and sinks, and the valve opens. Gas accumulated inside the trap is discharged, and then condensate is discharged with foreign substance through the valve. This frequency of valve opening increased or decreased by the amount of condensate inflow. When a large amount of gas such as air discharged through air vents of the bucket accumulates at the upper portion of the trap and pushes the water level inside the bucket, the bucket loses buoyancy and sinks, and open the valve to discharge gas.
Above is a complete operating cycle, and the cycle is repeated.
Movie
You need Windows Media Player to watch the movie. To download Windows Media Player, click the below link.
-
No condensate retention
-
No condensate retention since operated by specific gravity difference of steam and condensate.
-
Endurability
-
Original internal structure enables long service life.
As stated in the chart below, disc type steam trap will become not to able to stop steam within two years but internal bucket type has no change for steam loss over three years.
-
Energy Saving
-
Since air film of piping wall is removed by air intermittent operation, thermal efficiency is increased considerably. Moreover, compared with conventional type, compact and lightweight design of energy saving.
-
Strong for scale
-
Since its structure makes scale fine, the inlet strainer is not required in principle.
- Low tolerance for freeze.
- There are restrictions on installation direction, except for some model.
- Compared to disk type trap, the body is relatively larger.
- Lever type has abrasion partly.
(2) Float Type Steam Trap
Operation principle
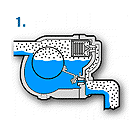
At start-up, since the float is down, the valve is closed. In this state, air in the system and piping is discharged out through the air vent which is opened. When condensate flows into the product, the float flows up and opens the valve, and then discharges condensate. Air is kept to be discharged out from the air vent.

When steam flows into the trap, inner pressure of the air vent rises by steam temperature, and the air vent is closed. According to the amount of condensate inflow, the float position moves up and down, at the same time opening degree of the valve changes, as a result, condensate is continuously discharged. When condensate inflow is out, the float moves down and closes the valve.

When air or non-condensable gas flows into the product, it accumulates in the upper part of the product. When temperature of air or non-condensable gas decreases with condensate inflow, the air vent opens and discharges it to outside of the trap.
Movie
You need Windows Media Player to watch the movie. To download Windows Media Player, click the below link.
-
No condensate retention
-
No condensate retention because this type of trap operates by specific gravity difference of steam and condensate as inverted bucket type
-
High tolerance for pressure difference
-
Operation is stable without influence of inlet pressure fluctuation or back pressure. Most suitable for condensate recovery.
-
Energy saving design
-
No steam loss because the valve seat is always sealed by water.
-
Quick warming up
-
Built-in bellows type air vent discharge air inside piping at the start of ventilation.
- Low tolerance for water hammer due to sealed float.
- Low tolerance for freeze.
- The body of lever float type is relatively large because of lever structure.
(3) Thermostatic Steam Trap
(a) Bellows type

At start-up, the bellows contracts and opens the valve to discharge air and condensate. Valve is kept fully open until steam flow in.

When steam flow into the trap, the liquid in the bellows sealed is heated to evaporate. When inside pressure increases, bellows inflates with balance to pressure in the trap and the valve is closed.
When air and condensate accumulate in the trap, and temperature becomes slightly lower than the saturation steam temperature, the valve contracts again to open.
Movie
You need Windows Media Player to watch the movie. To download Windows Media Player, click the below link.
- Exhaust perofrmance is good.
- Operation is quiet.
- Compact and lightweight.
- Condensate retention can be generated because operation starts at lower temperature than saturated steam temperature.
- Low durability for corrosion by fatigue of bellows.
- Low tolerance for water hammer.
(b) Bimetal type
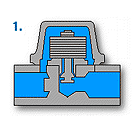
Thermostatic and bimetal type steam trap has two metal plates (called bimetal) of different thermal expansion coefficient are bonded. This trap uses them for the element part for use of nature that it is curved by heat.
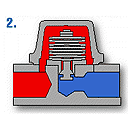
There are various shapes or combinations of plates by manufacturers for bimetal, adjustment is necessary for each steam pressure since the saturated steam temperature and temperature difference are required to operate the bimetal.
- Can control condensate temperature to be discharged.
- Good discharge performance of low temperature air.
- Operation is quiet.
- High tolerance for water hammer.
- Condensate retention can be generated because operation starts at lower temperature than saturated steam temperature.
- There is possibility of steam loss due to delay of valve close if adjustment is not enough.
- Low durability for corrosion by fatigue of bimetal.
(4) Thermodynamic Steam Trap
(a) Disc Type
Disc type steam trap has been widely used because it is small, lightweight, less mounting space and no restriction on mounting direction.
This type of trap has the advantage that simple and compact structure, such as moving part is disc only.


Air and condensate flow by the thermal jacket around a pressure change chamber, reaching the underside of the disc and pushing up the disc, then they are discharged to the outlet side.
Since steam which reaches the disc passes through the underside of the disk at high speed, the pressure drops at this part and the disc is closed. Steam pressure in the pressure change chamber leaks slowly and is reduced. As a result, the valve opens by the pressure at the underside of this disc. Condensate is discharged at this time, and the valve is closed immediately if the steam flows in.
Since the pressure change chamber is for steam jacket type, it is not affected by pressure fluctuation in the pressure change chamber by outside temperature and weather, and chattering is fewer.
Movie
You need Windows Media Player to watch the movie. To download Windows Media Player, click the below link.
- Compact and lightweight.
- Large tolerance for freeze.
- No limitation for installation direction.
- Usable for overheated steam.
- Ordinary disc type is easily influenced by outside temperature and may cause chattering.
- Since the trap basically operates by temperature, there is possibility of condensate retention.
Advice
There is no steam trap which can meet 100% of requirements.
In order to consider high efficient improvement and energy saving for a system, there are some points for selection.
- No condensate retention
- High tolerance for back pressure to recover condensate
- Intermittent condensate discharge for heat efficiency
Select the trap which can meet these three points, in addition, it is similarly important that the trap has no steam leakage, is superior in durability, and can be easily inspected and maintained.
As a conclusion, for disc type trap, initial cost is not expensive and plumbing work is easy but there are problems of condensate retention and tolerance for back pressure. For float type, it can works continuously and has large capacity but low tolerance for water hammer and freeze. For thermostatic type, operation is quiet but it cannot be used for fluid requiring large capacity. For inverted bucket type, it has good balance of various performances and can be installed in various places but has low tolerance for freeze. Since each trap has drawback and advantage, leave the selection to Yoshitake for appropriate trap.